Cervical Cancer
Cervical Cancer: Understanding, Symptoms, Causes, and Treatment Options
Cervical cancer is a disease of the cervix. This is the lower, smaller part of the uterus that connects to the birth canal. It's mainly caused by long-lasting infections with certain types of Human Papilloma Virus (HPV). HPV is easily spread by sexual contact. Mostly, HPV infections go away on their own. But some stay around and cause changes in the cervix cells. This can turn into cancer if doctors don't treat it. Early cervical cancer usually doesn't cause symptoms. But, late cervical cancer can cause pelvic pain and bleeding. The good news? We can stop cervical cancer with regular Pap and HPV tests. Precancerous changes occur in the cervix before they become cancer. The HPV vaccine is also good for prevention. It greatly reduces infection risk from HPV types that cause most cervical cancers. Finding cervical cancer early and treating it right away massively improves outcomes
Book an Appointment
What are Cervical Cancer Symptoms?
Cervical cancer in starting phases may remain symptomless. As it grows, look out for these signs:
- Unexpected vaginal bleeding (after sex, between menstrual cycles, or post-menopause)
- Odd vaginal discharge (liquid-like, blood-filled, or awful smelling)
- Pain in the lower tummy or pain during sex
- Such signs can be symptoms of other medical issues, but any peculiar body changes need swift examination by a medical expert.
The chances of successful treatment rise hugely if detected early through assessment and frequent health check-ups
Types of Cervical Cancer
Generally, there are two types of cervical cancer:
- Squamous Cell Carcinoma: This is flat-cell cancer, and it's the most common. It represents a whopping 80-90% of all cases! It starts from the skinny, flat cells on the cervix exterior, called squamous epithelium.
- Adenocarcinoma: This one is mucus gland cancer and it's less common, only covering 10-20%. It grows in cervical mucus making cells. Because it's higher up in the cervix canal, it's harder to find.
Each one needs its own treatment method. So, making the right diagnosis is super important
Causes of Cervical Cancer in Females
The primary cause of cervical cancer in females is infection with certain high-risk strains of HPV mainly 16 and 18. Other risk factors that may increase the likelihood of developing cervical cancer include:
- Smoking: It harms cervical cells and increases the risk.
- Low Defense System or low immunity: Makes it hard for the body to battle HPV infections.
- Oral Contraceptives: Using these for a long time can heighten the risk.
- Early Start of Sexual Activity: Amplifying HPV exposure early on.
- Several Partners or High Risk Sexual Behavior: Leans towards a higher HPV infection chance.
- Cervical Cancer in Family: Genetics could be influential in a few cases.

Book an Appointment
Diagnosis and Testing of Cervical Cancer
Spotting cervical cancer early is key for effective treatment. There are several methods to find any changes in the cervix that could be precancerous or cancerous:
- Pap Smear Test: This is a regular test that collects cells from the cervix. It helps to find any unusual changes early, which means treatment can start sooner.
- HPV DNA Test: This test checks for HPV types that are often linked with cervical cancer. It can find people who are at higher risk before any cellular changes start.
- Colposcopy: If a Pap smear shows something unusual, a colposcopy is done. It uses a special magnifying device to get a closer look at the cervix. This way, any cellular changes can be seen more clearly.
- Biopsy: If needed, a biopsy takes a small piece of cervical tissue. It's then analyzed in a lab. This test gives a clear diagnosis and lets us know the specific type of the cancer.
Using these tests together helps to catch any issues earlier. This allows for quick and focused treatment options.
Stages of Cervical Cancer in Women
Cervical cancer in women progresses through five stages, each indicating the extent of the cancer's spread:
- Stage 0: Known as carcinoma in situ, this early stage features abnormal cells on the cervix’s surface, which could potentially become cancerous but have not yet invaded deeper tissues.
- Stage I: At this stage, cancer is confined to the cervix and has not spread to nearby tissues. It may be small (IA) or larger and more invasive (IB), but remains localized.
- Stage II: The cancer now goes beyond the cervix. It has moved to close areas like the upper part of the vagina or tissues nearby. However, it hasn't gotten to the pelvic wall or the bottom third of the vagina.
- Stage III: Now, the cancer has grown more. It could be in the lower vagina or the pelvic wall. It might even block the ureters, which join the kidneys and bladder, and can change how the kidneys work.
- Stage IV: This is the last stage. Here, the cancer has traveled to far-off organs like the bladder or rectum (IVA). It can also go beyond the pelvic region to distant organs such as the lungs, liver, or bones (IVB).
Understanding the stage of cervical cancer is crucial for determining the appropriate treatment and assessing the prognosis.
Does Cervical Cancer Spread Quickly?
Cervical cancer usually takes its time to develop. This makes routine tests, like Pap smears and HPV exams, really helpful in finding it early and treating it. Changes that can turn into cancer in cervical cells can take a while — years, even. This gives us plenty of time to treat it before it becomes serious. But, if not found or treated, some aggressive types like certain squamous cell carcinoma or adenocarcinoma could quickly spread. They could reach your nearby tissues, lymph nodes, and other organs. Constant testing is key. It can stop cervical cancer from advancing and manage it before it gets worse.
Book an Appointment
Treatment for Cervical Cancer
Dealing with cervical cancer isn't a one-size-fits-all situation. It rides on factors like what phase the cancer is, its size, and the patient's general well-being. Main treatment plans encompass:
- Surgery: Early-stage cervical cancer often meets its match with surgery. The process can involve eliminating cancer cells or doing away with the whole cervix and uterus (hysterectomy). Isn't that a relief?
- Radiation Therapy: Advanced cases require radiation therapy. It's all about using X-rays that pack a punch to wipe out cancer cells. It often goes shoulder to shoulder with chemotherapy.
- Chemotherapy: This method employs potent drugs to wipe out cancer cells. It features a lot in later stages or blends well with radiation therapy.
- Targeted Therapy and Immunotherapy: These hotshots of treatment are fresh on the scene. They zero in on exact parts of cancer cells or beef up the immune system to take on cancer.
Procedure of Cervical Cancer Treatment
Before Surgery
Before the surgery, patients usually have a bunch of tests. They check if you are healthy and the extent of cancer spread. These include blood tests, scans and a thorough physical check up. The doctors also give you a list of do's and don’ts before the big day, like no eating or maybe changing your medicines a bit. Stick to this and you'll have a nice recovery. That gets you ready to get the most from your surgery.
During Surgery
There are different types of procedures for cervical cancer, depending on its type and stage. Here are a few examples:
- Conization: This process involves taking out a cone-shaped tissue piece, usually for cancer in the early stages.
- Radical Hysterectomy: This is a surgical step where the uterus is removed along with adjacent tissues and lymph nodes, based on how far the cancer has progressed.
- Radical Trachelectomy: In this procedure, the cervix, a part of the vagina, and the nearby tissues and lymph nodes are removed. This is typically for early-stage cancer and is done with the intention of keeping fertility intact.
- Pelvic Exenteration: This extensive surgery involves removing nearby organs impacted by advanced cancer. This is often the choice when the cancer has not disappeared completely or has reappeared after prior radiotherapy and chemotherapy. The surgery selected is adapted to the patient's individual condition and objectives.
After Surgery
After-surgery care is key for getting better. Helping the body heal means no heavy exercising for six weeks. You might get painkillers too. Frequent check-ups are a must to see if you're healing well, deal with problems, and make sure the disease doesn't return, which helps ensure ongoing wellness.
Cervical Cancer Surgery Recovery Time
Healing time following cervical cancer surgery isn't the same for everyone. It hinges on the procedure used. Minor surgeries might need close to two weeks to recover. Major ones like a thorough hysterectomy might need upwards of six weeks. Following doctors' post-operation directions and going to check-up meetings are vital. They promote correct healing and stop problems from happening.
Cervical cancer is a serious condition, yet it can be dealt with effectively when noticed early and acted on swiftly. Recognizing the signs, kinds, origins, and methods of treatment allows ladies to make knowledgeable choices for their well being and care.
Book an Appointment

Why Choose Dr Sarita for Cervical Cancer Treatment?
Meet Dr. Sarita Kumari as a well-known Gynaecologic Oncologist and Oncosurgeon. She just not only understands Surgical and Gynecologic Oncology, she excels in it. Her degree trio of MBBS, MD, and MCh is from AIIMS, New Delhi. She's a pro at tackling tough cases, like cervical cancer. Training at a top Indian medical institute prepped her for leading patient care at Max Healthcare. Dr. Kumari is all about the individual. She designs unique treatment schedules fitted flawlessly to patient needs. Modern medical methods are her tools for administering care with kindness. When you choose Dr. Sarita Kumari you're choosing a beacon in the medical field, committed to the greatest outcomes for her patients.
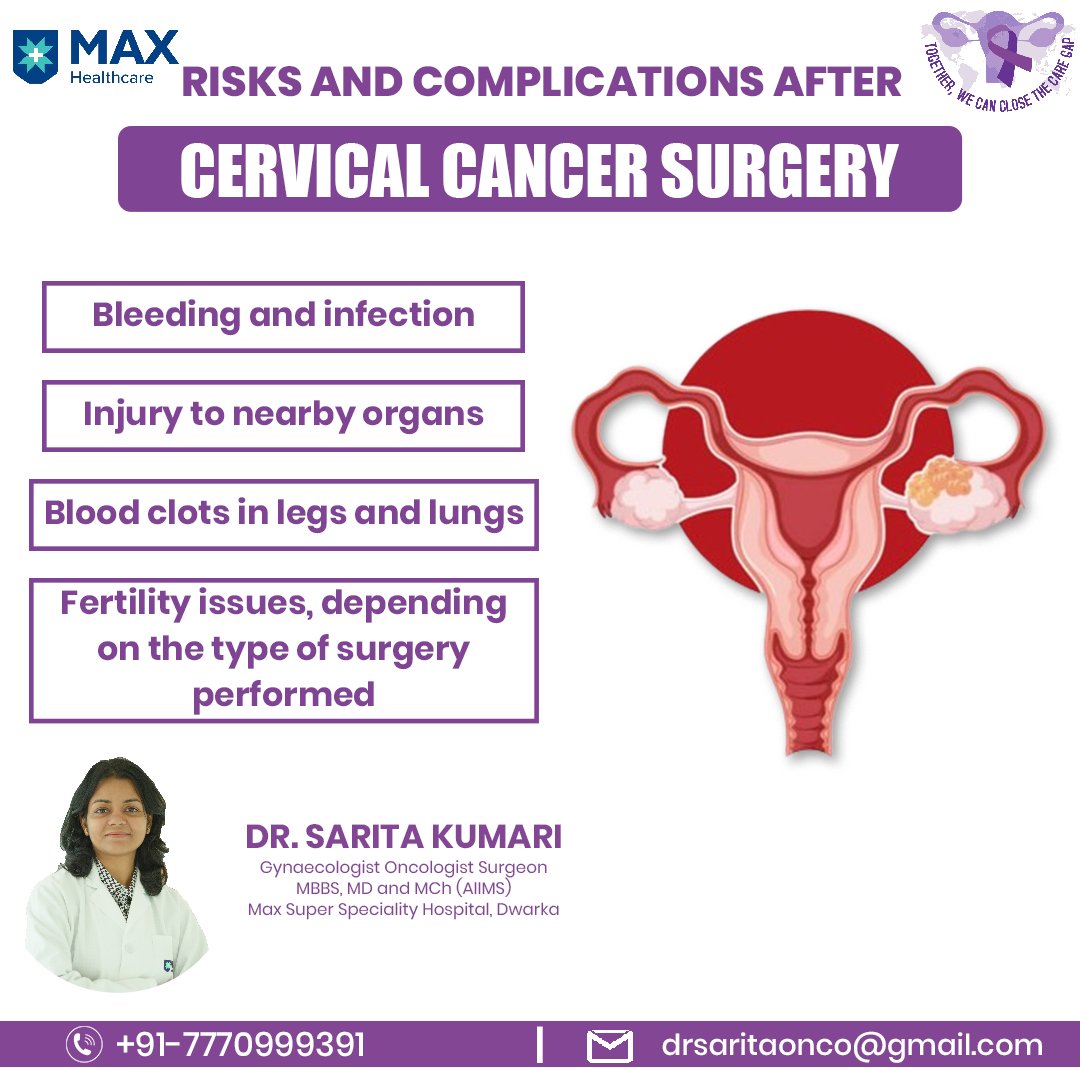
Risks and Complications of Cervical Cancer Surgery
As with any surgery, there are risks associated with cervical cancer treatment, including:
- Bleeding and infection
- Injury to nearby organs
- Blood clots in legs and lungs
- Fertility issues, depending on the type of surgery performed
Each patient’s risks will vary, and the healthcare team will provide guidance on how to manage these potential complications.