Ovarian Cancer
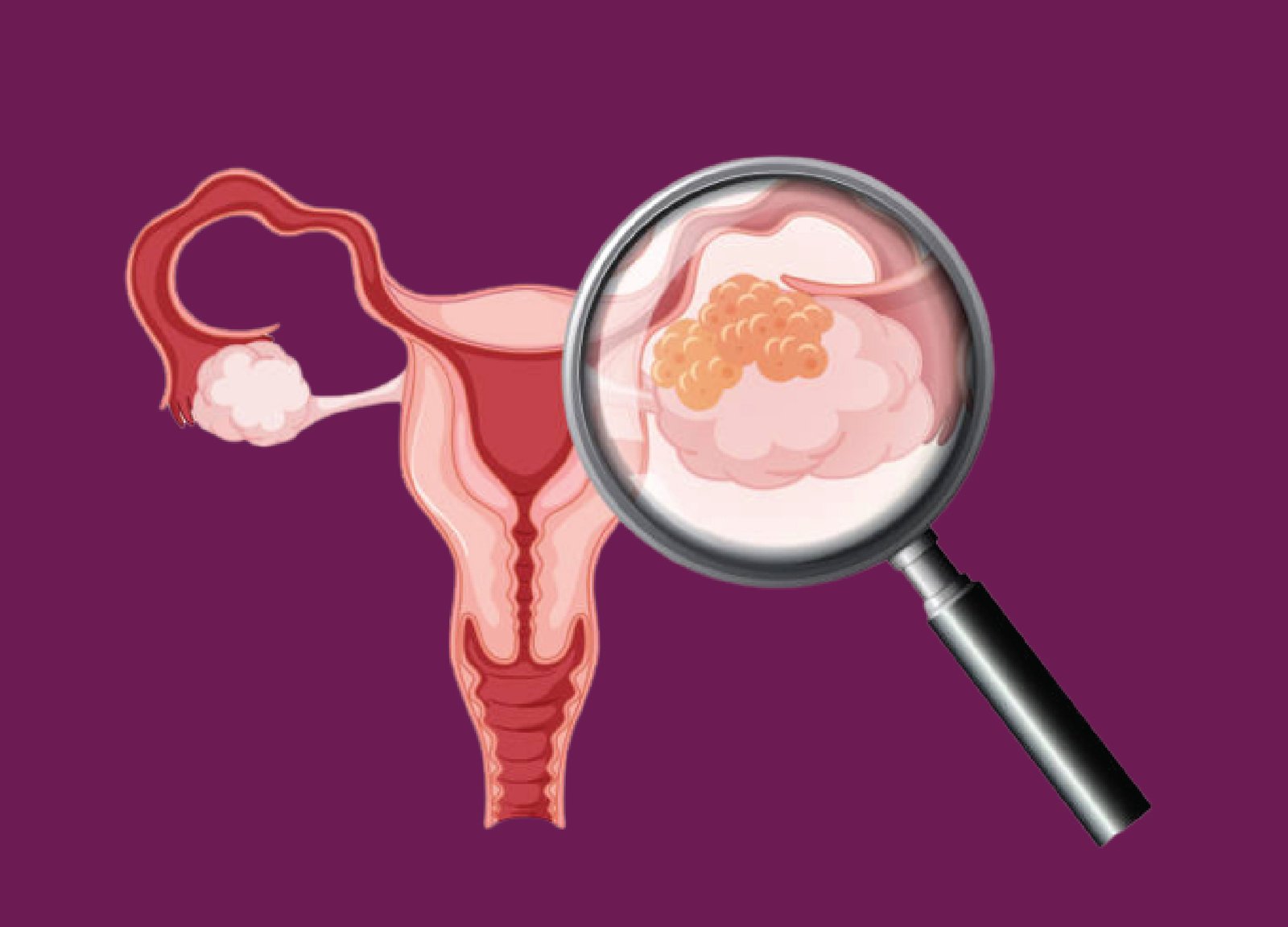
Ovarian Cancer: Understanding, Detecting, and Treating This Serious Condition
Ovarian cancer is a big health issue needing quick checks and special care for the best results. It's an often-seen cancer in women, getting first caught when it's already grown. That's why knowing about it and catching it early is super important. At Dr. Sarita Kumari’s place (MBBS, MD, and MCh from AIIMS, New Delhi), we're all about full support, top-notch guidance, and caring service. If you’re looking for the best ovarian cancer Doctors in Delhi or Gurgaon near me, then it is your go-to place to learn about ovarian cancer, finding symptoms, understanding tests, looking at cure methods, plus tips on handling daily life in and after treatment.
Book an Appointment
What is Ovarian Cancer?
Ovarian cancer starts in the ovaries, the parts of a woman's body that make eggs and important hormones like estrogen and progesterone. It happens when odd cells grow rapidly in or around the ovaries, creating tumors. These cancer cells don't die off like regular cells do. Instead, they build up and create blocks, messing up how the ovaries are supposed to work.
If ovarian cancer isn't treated quickly, it can spread from the ovaries to nearby body parts like the belly or lymph nodes. This spread makes fighting the disease harder. It's important to spot ovarian cancer early. Symptoms often get missed in the beginning. Regular doctor visits can help catch it early. Being aware of the signs can help people get the help they need sooner. This early help can make treatment more likely to work and make it easier to handle the disease
Types of Ovarian Cancer
Ovarian cancer springs from different cells in the ovaries. Each has unique traits that shape treatment plans and results.
- Epithelial Tumors: They account for about 90% of ovarian cancer cases. These tumors start in the ovaries' outer cell layer. Older women usually have them and are often undiscovered until they're far more advanced. This calls for a stronger treatment method.
- Germ Cell Tumors: These aren't your typical tumors. They begin in the very cells that create eggs. It's the younger women who most often see these, and the good news? They usually respond well to therapy.
- Stromal Tumors: They're an uncommon ovarian cancer type, starting in the ovary's hormone-making tissue. Due to symptoms linked with hormones, such as irregular periods or hormone imbalance signs, stromal tumors are typically spotted earlier. This leads to quicker medical checks and therapy.
Knowing the particular kind of ovarian cancer—epithelial, germ cell, or stromal—is significant for developing a successful treatment strategy. Each type has a different reaction to treatments; a precise diagnosis is vital for the greatest potential result
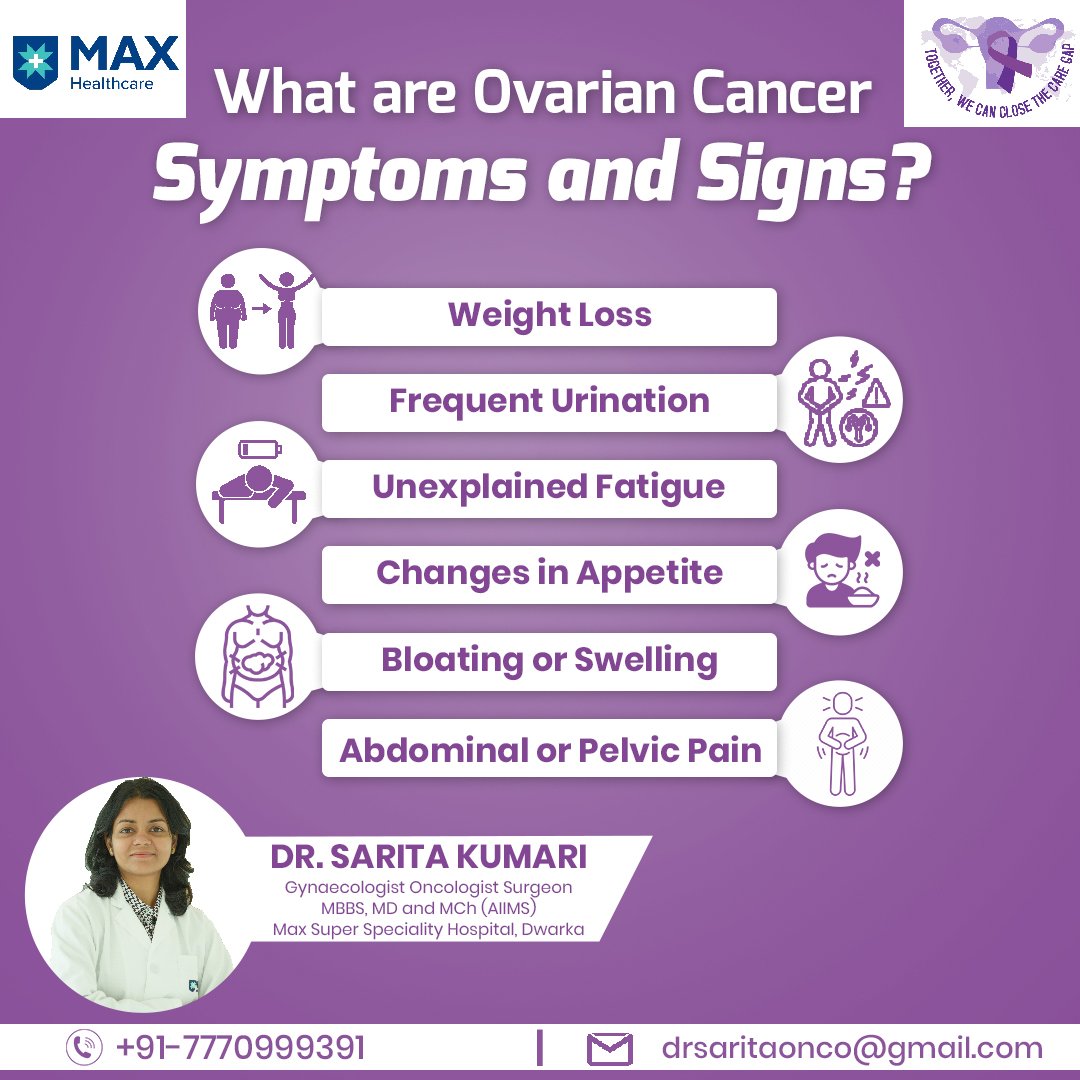
What are Ovarian Cancer Symptoms and Signs?
Ovarian cancer symptoms can be subtle and easily mistaken for digestive or menstrual issues, making early detection a challenge. Common symptoms include:
- Abdominal or Pelvic Pain: Persistent pain in the tummy or bikini region.
- Bloating or Swelling: Frequent bloating or swelling of the tummy that does not go away.
- Changes in Appetite: Feeling full quickly or experiencing a loss of appetite.
- Frequent Urination: Needing to pee more often than usual.
- Unexplained Fatigue: Feeling tired or low on energy without a clear cause.
- Weight Loss: Unintended weight loss can sometimes occur with ovarian cancer.
If you experience any of these symptoms for more than two weeks, it is essential to consult a specialist for a thorough evaluation
Book an Appointment
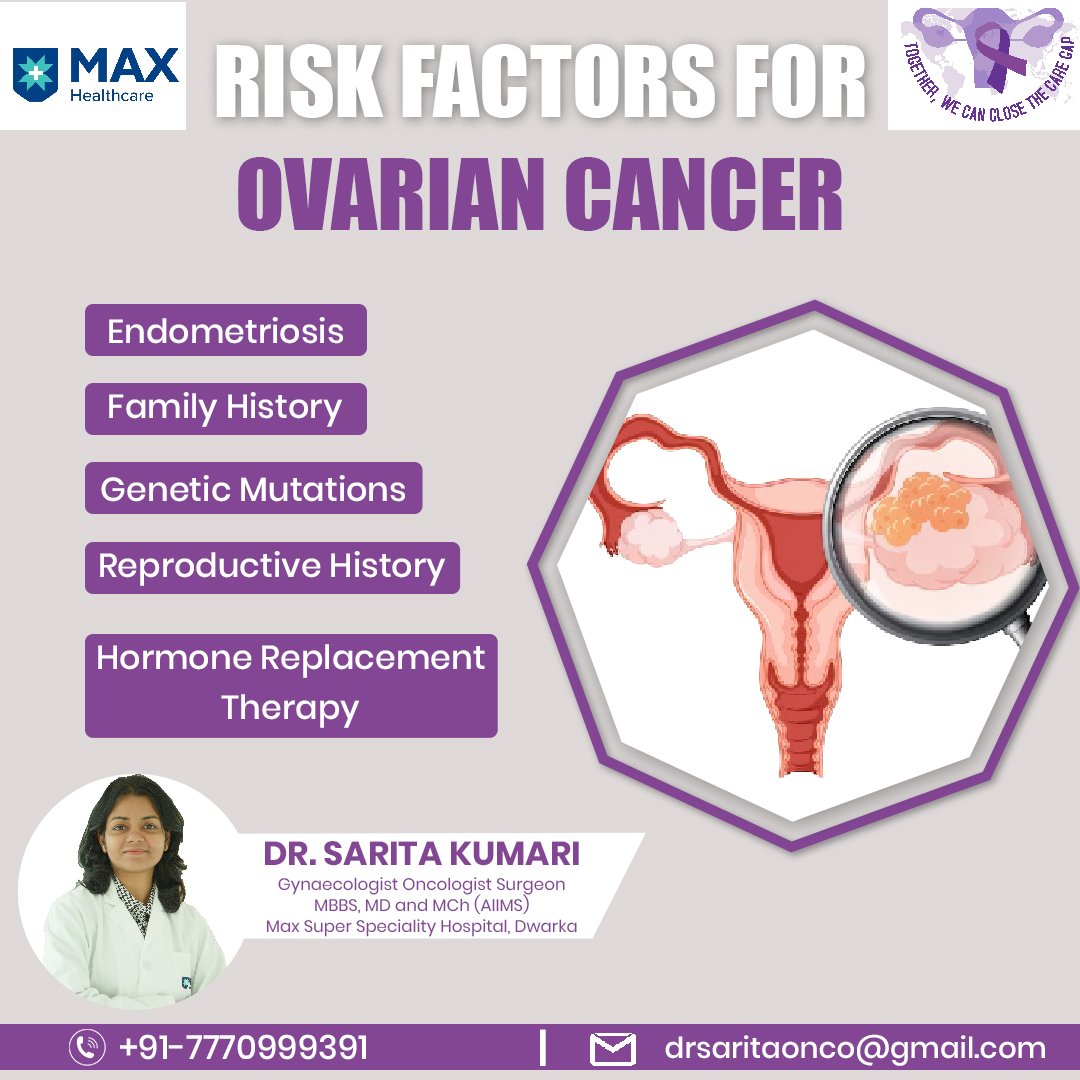
Risk Factors for Ovarian Cancer
There are certain factors which increase the risk of getting ovarian cancer. Important among these are:
- Age: Ovarian cancer often happens to women over 50.
- Family History: A family history of ovarian, breast, or colon cancer can elevate your risk.
- Genetic Mutations: Mutation in genes like BRCA1 and BRCA2 can add to your risk. A simple blood test can find these mutations.
- Reproductive History: Women who haven’t given birth or had children later in life may face a slightly higher risk.
- Hormone Replacement Therapy: Long-term use of hormone replacement therapy after cessation of menses can increase risk.
- Endometriosis: Women with long standing endometriosis, a condition where uterine tissue grows outside the uterus, may be at a higher risk.
These signs can seem like minor issues, so we might miss them. But, if they stick around for more than two weeks or get worse, it's important to see a specialist. They can check things out properly. Catching it early means treatments can work better, and the odds of a good result can go up
How Long Does it Take to Detect Ovarian Cancer?
Spotting ovarian cancer early boosts the success of treatment. If there's a suspicion of ovarian cancer, a number of tests help decide if it's present or not:
- Physical Examination: First up, often it's a pelvic exam. It gives doctors a way to find any changes in the ovaries or areas around them.
- Imaging Tests: Tests like ultrasound, MRI and CT scans are common tools to see the ovaries and things close by. The transvaginal ultrasound shares clear pictures - it's a superstar at helping doctors pinpoint possible issues.
- Blood Tests: The CA-125 blood exam identifies the concentration of a specific protein that could rise in ovarian cancer. Even though CA-125 isn't exclusive to ovarian cancer, it offers insights and assists in tracking treatment improvements. Different types of tumors produce different proteins which are raised in blood and help in early diagnosis.
- Biopsy: If scans and blood exams suggest possible cancer, a tissue sampling might be carried out in advanced stages to obtain sample tissues for examination. This sampling is the singular method to accurately confirm an ovarian cancer diagnosis.
Different Stages of Ovarian Cancer
Ovarian cancer is classified into stages that indicate how far the ovarian cancer has spread. Staging helps determine the appropriate treatment approach:
- Stage I: Cancer is limited to one or both ovaries.
- Stage II:Cancer has spread to nearby pelvic structures, like the fallopian tubes or uterus.
- Stage III: Cancer has reached the abdomen, potentially affecting the abdominal lining or lymph nodes.
- Stage IV: Cancer has spread beyond the abdomen to distant organs, such as the liver or lungs.
Doctors use stages to pick the right treatment plan and understand potential outcomes. A high stage means the cancer is advanced, often needing tougher treatment. If we find cancer early, we can usually treat it better. This shows why it's key to catch it in time
Book an Appointment
Common Treatments for Ovarian Cancer
Treatment for ovarian cancer is tailored to the individual’s needs, including cancer type, stage, and overall health. Common treatment options include:
Surgery
Surgery is often the first step in treating ovarian cancer. The goal is to remove the tumor, staging the disease, and achieving optimal debulking of tumor.
Surgical Considerations:
1. Patient's overall health.
2. Tumor size, location, and spread.
3.Tumour type and grade.
4. Fertility-sparing options i.e. conservation of uterus and one ovary and tube (for younger patients).
Surgical Objectives:
1. Staging: Determine the extent of disease spread.
2. Cytoreduction: Remove all visible disease.
Types of Surgery:
1. Laparotomy (open surgery): Exploratory surgery to remove tumor tissue.
2. Laparoscopy (minimally invasive): For early-stage disease or staging.
3. Robotic-assisted surgery: Enhanced precision and minimal invasiveness.
4. Surgery is often combined with Hyperthermic Intraperitoneal Chemotherapy (HIPEC) for decreasing the chances of cancer coming back or dying from cancer.
Surgical Procedures:
1. Peritoneal washing: Examining fluid for cancer cells.
2. Hysterectomy: Removing the uterus.
3. Bilateral Salpingo-Oophorectomy (BSO): Removing ovaries and fallopian tubes.
4. Omentectomy: Removing fatty tissue.
5. Lymphadenectomy: Removing affected lymph nodes.
6. Cytoreductive Surgery: Removing all visible tumor tissue. This may include a) Intestinal resection: removing affected intestine segments and, b) Diaphragmatic stripping: removing tumor from diaphragm or other organs depending on whether they are involved by tumor
Potential Risks and Complications:
1. Infection.
2. Bleeding.
3. Bowel obstruction.
4. Urinary tract injury.
5. Lymphedema or leg edema.
Questions to Ask Your Doctor:
1. What type of surgery is best for me?
2. What are the risks and benefits?
3. How will surgery affect my daily life?
4. What are the next steps after surgery?
Remember:
1. Surgery is often the first step in treatment.
2. Multidisciplinary care teams ensure good outcomes.
3. Ask questions and seek support
What is HIPEC?
HIPEC is a specialized treatment that combines heat and chemotherapy to target cancer cells in the abdomen.
How does HIPEC work?
1. During surgery, heated chemotherapy is circulated through the abdominal cavity for 30-90 minutes.
2. The heat helps chemotherapy penetrate deeper into tissue, killing cancer cells.
3. This treatment targets microscopic cancer cells and small tumors.
Benefits of HIPEC for Ovarian Cancer
1. Improves survival rates and reduces recurrence.
2. Enhances effectiveness of surgery.
3. Reduces cancer spread.
4. Minimizes side effects compared to traditional chemotherapy.
Is HIPEC right for me?
You may be a candidate if:
1. You have advanced ovarian cancer.
2. Cancer has spread to the abdominal cavity.
3. You're in good overall health.
Look for:
1. Experienced gynae oncosurgeons and medical oncologists.
2. Specialized centers with HIPEC expertise.
Questions to Ask Your Doctor
1. Is HIPEC suitable for my ovarian cancer stage?
2. What are the benefits and risks?
3. How will HIPEC affect my quality of life?
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy, the use of potent drugs aimed at eliminating cancer cells, is frequently administered following ovarian cancer surgery. The goal is to kill off unseen remaining cells and lower the reappearance risk. If surgery isn't an option, chemotherapy becomes the main treatment. Paclitaxel and carboplatin are typical chemotherapy drugs applied to ovarian cancer, often combined for better results. By focusing on rapidly multiplying cells, these drugs aid in halting cancer progression and enhancing patient prognosis.
Targeted Therapy
Ovarian cancer treatment now includes drugs that directly combat the growth of cancer cells, leaving healthy cells unharmed. This sharp approach cuts down on side effects, unlike old-fashioned chemotherapy. One effective kind of targeted therapy is PARP inhibitors. They work really well for patients with BRCA gene mutations. These stoppers keep cancer cells from fixing their own DNA. This causes them to die and slows down cancer growth. This new focused therapy gives hope for custom treatment. It makes care more effective and improves life quality for many dealing with ovarian cancer.
Immunotherapy
Immunotherapy is an emerging option for certain types of cancer, including ovarian cancer. This treatment harnesses the body’s immune system to detect and destroy cancer cells. Although still under study, immunotherapy may be an option in cases where other treatments have not been effective.
Hormone Therapy
Ovarian cancer sometimes relies on hormones like estrogen to grow, and hormone therapy helps. The therapy either blocks the hormone signals cancer cells use to grow or decreases the body's hormone levels. By doing this, hormone-driven cancer might grow slower. If hormones fuel the cancer, doctors often consider hormone therapy. They can pair it with other treatments, such as surgery or chemo. The goal? Target the cancer more precisely and maybe lessen side effects than harsher treatments
Living with Ovarian Cancer: Support and Care
If you’re looking for the answer of what is life after the diagnosis of ovarian cancer? Then, an ovarian cancer diagnosis can be daunting, yet it's crucial to remember help isn't far away. Life demands physical and emotional balance with ovarian cancer, involving routine check-ups and lifestyle shifts. The clinic led by Dr. Sarita Kumari offers full support to guide you through this journey.
Coping with Treatment
A good number of people feel tired, sick feeling, and grapple with feelings while getting treatment. A knowledgeable team, knowing the hurdles of ovarian cancer, can aid you to deal with side effects, getting supportive care.
Support Systems
Feeling loved by relatives, pals, and therapists can change everything. Joining a support group for folks with ovarian cancer creates a special bond. You meet people who really understand your journey.
Who is the Best Ovarian Cancer Specialist?
Dr. Sarita Kumari is a top pick for ovarian cancer treatment in India. She boasts impressive qualifications and loads of experience. She holds an MBBS, MD, and MCh from AIIMS, New Delhi, a respected institution. She is one of the best ovarian cancer Doctors in Delhi and Gurugram. She has been trained in cytoreductive surgery and HIPEC in India and in prestigious oncology centers abroad (Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, USA; Jikei University School of Medicine, Japan; Charite Comprehensive Cancer Center, Berlin) Her focus is maximum surgical effort to ensure no visible tumor at the end of surgery. Dr. Sarita Kumari works fully centered on her patients. She provides modern treatments like small-invasive surgery, fertility sparing surgery, focused therapy, and personalized treatment options. Continually catching up on the latest medical developments, she customizes care to fit patient needs. Showing care and commitment, Dr. Sarita Kumari's skill and track record make her a go-to for managing ovarian cancer with top-notch care.


